Introduction to the Magento template engine
A template engine is a mechanism for rendering HTML output from templates associated with page layout blocks. The Magento template rendering subsystem can support multiple template engines, including the default PHP-based engine for processing PHTML templates.
This article describes the design of the Magento template rendering subsystem and the implementation of the default template engine, and provides instructions on how to add a custom engine to support templates other than PHTML.
How the Magento template engine renders HTML output
A template engine is invoked during page layout processing. Any page layout is a hierarchy of containers, which are placeholders for content, and blocks, which actually generate content. Each block corresponds to a certain Magento PHP class.
All block classes are inherited from either Magento\Framework\View\Element\AbstractBlock or Magento\Framework\View\Element\Template (which in its turn is inherited from AbstractBlock).
The difference between these two classes is that the Template class has methods required to work with templates and allows initiating a template engine to generate HTML content based on a template, while AbstractBlock has no methods for working with templates, and provides only displaying the hard-coded HTML content:

The AbstractBlock class implements the main toHtml() method, which is called by all blocks when it is necessary to generate the HTML output.
The sequence of execution of toHtml() depends on whether the HTML content was previously cached:
-
Case 1: HTML was previously cached:
-
Load the cached HTML content.
-
Perform the HTML content post-processing defined in
_afterToHtml().
-
-
Case 2: HTML was not previously cached:
-
Perform the preparatory tasks defined
in _beforeToHtml(). -
Generate the HTML content. Here is where the template engine is invoked for blocks with templates: if a block class is inherited from the
Templateclass, and has a predefined or dynamically obtained template name, then generating the HTML content is performed by callingTemplate::fetchView()which initiates the template engine, calls therender()method, and returns the HTML content for subsequent processing byAbstractBlock::toHtml(). -
Cache the generated HTML.
-
Perform the HTML content post-processing defined in
_afterToHtml().
-
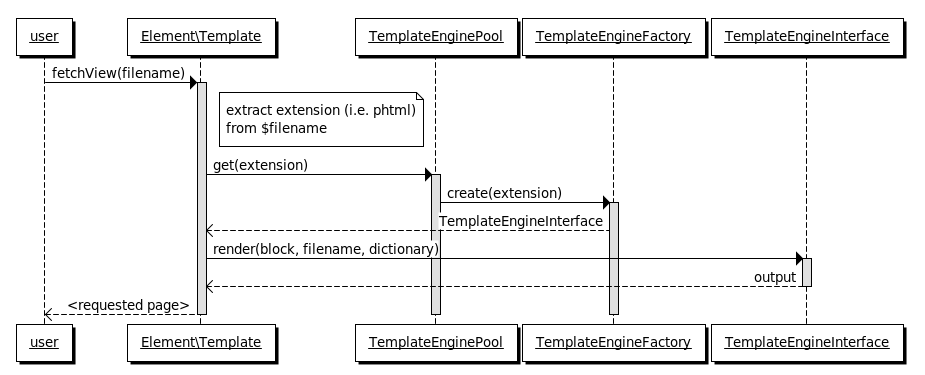
Schematically, a template engine performs the following (Case 2, step 2):

The same process, with more technical details:
Invoke a PHTML block from a PHTML block
The following diagram illustrates the actions executed when a PHTML block is invoked from a PHTML block by a getChildHtml call.
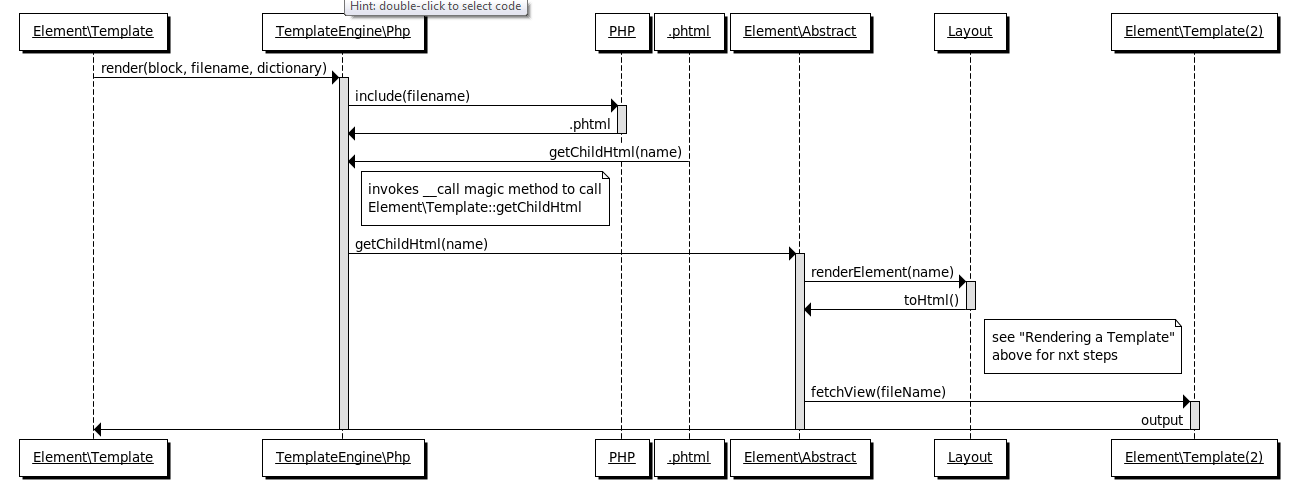
Example of a getChildHtml call:
<?php echo $this->getChildHtml('product_type_data') ?>
Template rendering
Template files rendering is performed by \Magento\Framework\View\TemplateEngine\Php:
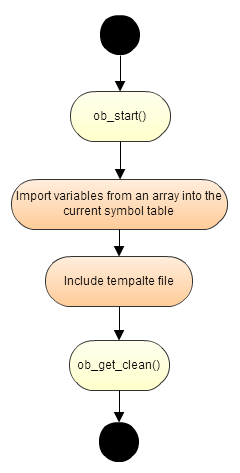
Template engine file structure
All template engine files are stored in the View library:
_lib/Magento/View |--TemplateEngineFactory.php |--TemplateEngineInterface.php |--TemplateEnginePool.php |_/Element |--AbstractBlock.php |--Template.php |_/TemplateEngine |--Php.php
The default engine for working with templates is the Magento\Framework\View\TemplateEngine\Php class.
Basic classes
The class diagram of the basic classes Implement the template rendering subsystem:
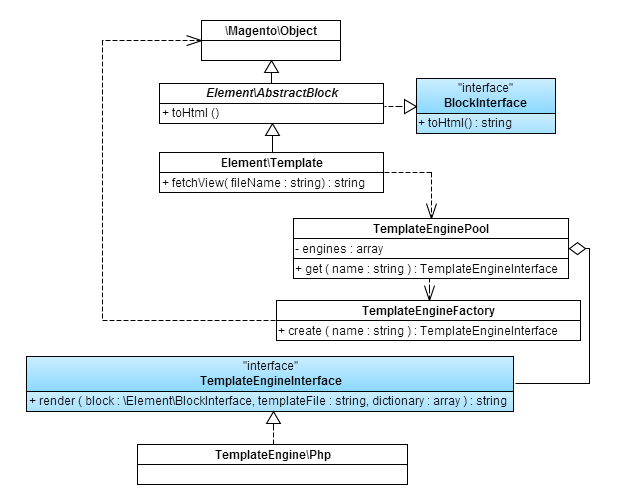
Class descriptions
Reviewer: Please verify all of this information
This section discusses the following classes:
- Magento\Framework\View\Element\Template
- Magento\Framework\View\TemplateEngineFactory
- Magento\Framework\View\TemplateEnginePool
- Magento\Framework\View\TemplateEngineInterface
- Magento\Framework\View\TemplateEngine\Php
Magento\Framework\View\Element\Template
Magento\Framework\View\Element\Template is the starting point for template rendering. To initiate the rendering process, Template::fetchView() is invoked with the name of the template file. It starts by extracting the template file extension and passing it to Magento\Framework\View\TemplateEngineFactory. On receiving an instance of Magento\Framework\View\TemplateEngineInterface, it calls the render() method and passes the rendered output to the caller.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
fetchView($fileName)
|
Retrieve the block view from the file (template).聽 |
getTemplateFile()聽
|
Get the absolute path to the template.聽 |
setTemplate($template)聽
|
Set a path to the template used for generating the block output.聽 |
getTemplate()聽
|
Get relevant path to the template.聽 |
Magento\Framework\View\TemplateEngineFactory
The create() method in Magento\Framework\View\TemplateEngineFactory receives the file extension, and constructs an instance of Magento\Framework\View\TemplateEngineInterface that implements the appropriate template engine.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
create($name)
|
Retrieve a template engine instance by its unique name. |
Magento\Framework\View\TemplateEnginePool
Magento\Framework\View\TemplateEnginePool maintains the list of all template engines available in the system. It uses the template engine factory to construct a template engine instance upon the first request.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
get($name)
|
Retrieve a template engine instance by its unique name. |
Magento\Framework\View\TemplateEngineInterface
Magento\Framework\View\TemplateEngineInterface defines the聽render()method. The resulting markup generated by the template engine is not sent directly to the output buffer, but it is returned to the caller.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
render( \Magento\Framework\View\Element\BlockInterface $block, $templateFile, array $dictionary = array() ) |
Render the specified template in the context of a particular block and with聽the data provided in $vars. |
Magento\Framework\View\TemplateEngine\Php
Magento\Framework\View\TemplateEngine\Php handles PHTML files, which use PHP as a templating language. In its render()聽implementation, it invokes include() to execute the PHP code contained in the template file. This means that PHP code in a template file must be written assuming that it will not be included to the template鈥檚 associated block class.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
render(
BlockInterface $block,
$fileName,
array $dictionary = array())
|
Include the specified PHTML template using the given block as $this reference, though only public methods are accessible.聽 |
Customize the template rendering subsystem
The Magento template rendering subsystem supports the following:
- Your module can introduce a new template engine.
- You can use PHTML templates together with other kinds of templates.
- You can embed any block to other blocks regardless of the underlying template engine.
Add a new template engine
To add support for a new template engine:
- Save the template engine code base in your Magento instance directory.
- Create a new implementation of Magento\Framework\View\TemplateEngineInterface. This class is used to initialize the underlying template engine, and must also implement the
render()function responsible for invoking the template engine on the given template file. - Register a newly introduced engine class through the DI configuration to process template files of a certain type as follows:
<config>
<type name="Magento\Framework\View\TemplateEngineFactory">
<param name="engines">
<array>
<item key="{template_extension}">
<value>{engine_class}</value>
</item>
</array>
</param>
</type>
</config>
Where:
{template_extension}is the type of template files, which are to be processed by the template engine. For example,phtml{engine_class}is the name of the class that implements a template engine
Example of a dependency injection configuration file:
Find us on